Case study about a MSW sorting facility in Italy – Eco+Eco Srl
The full report “Case study about MSW sorting facility in Italy – Eco+Eco Srl”
This report is part of a series of reports to explore lessons on sorting technologies for waste in the field of material and energy valorisation of waste within the framework of IEA Bioenergy Task 36. The purpose is to showcase examples from which countries can get inspiration and support in implementing solutions in the waste/resource management and Waste-to-Energy sector that would facilitate their transition towards circularity.
This report presents a mixed waste sorting facility in Italy, Eco+Eco srl, based in Fusina, near Venice (Italy). It manages unsorted municipal solid waste (MSW) generated in the province of Venice, characterized by a high urbanization and an impressive touristic pressure. Eco+Eco is currently authorised to treat up to 258,500 ton/year of waste. After first sorting processes to sort out metals and inert aggregates (i.e., gravel, sand, glass, and ceramics), the facilities convert remaining MSW into Solid Recovered Fuel (SRF). An approximate amount of 0.4 – 0.5 tons of SRF is produced from a ton of MSW. The SRF is used to either generate electrical power directly on site or is sold as fuel to other plants or cement kilns.
Download the report Summary “Case study about MSW sorting facility in Italy – Eco+Eco Srl”
The current process converts the remaining MSW in two separated SRF lines (L1 and L2). At present SRF Line 1 produces bio-stabilised waste (RDF) which is only partially treated in SRF Line 2 for the upgrading to SRF of class 3.3.2., while the remaining residual part is treated outside the plant. The SRF production plant is currently being revamped and it is expected that by the end of 2025 it will be able to sort out almost 6,000 t/year of plastics from the incoming MSW. The biogenic carbon content of the produced SRF is now around 60% of total carbon content, but it is likely that it will increase after the preliminary sorting of plastic materials. This will also increase the share of renewable energy produced from the SRF.
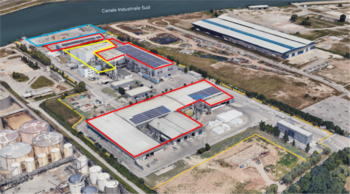
Figure. The industrial area of Eco+Eco Srl (in orange). The three operational MSW processing areas are: the transfer area (in blue), the SRF production and treatment area (in red) and the co-incinerator area (in yellow).
SRF is co-incinerated to produce steam for turbines which generate electricity for the self-consumption of the entire plant as well as the neighbouring companies. At present only 30% of the produced SRF is used to generate electricity, while the remaining part is sent to other local energy recovery facilities or cement kilns and/or power plants mainly located in East Europe. A second co-incinerator line is planned to be operational in 2026 and then all the SRF will be used in situ for energy production. The first co-incinerator line produces up to 20 MWth; with the start-up of the second co-incinerator line, the combined combustion potential will increase up to 47.9 MWth.
Revamping and upgrading of the plant will drastically reduce fossil fuel consumption thanks to automatization and by reducing material transport by trucks within and outside the plant. The upgrading will also decrease auto-power consumption and will make the management and the maintenance of the plant easier. The improvement in progress will allow to:
- recover a larger quantity of recyclable material from the MSW prior the energy recovery (e.g., around 6,000 ton/year of plastics),
- reduce the amount of material sent to co-incineration, by coupling the bio-stabilization process and the new more efficient sorting technology for material recovery,
- increase the calorific value of the produced SRF up to 35% compared to untreated original MSW,
- improve the co-incineration process, flue gas treatment and bottom ashes quality (which can be used in construction industry), with the SRF being more homogeneous than the untreated residual MSW;
- reduce the combustion of fossil-derived plastics, decreasing the related fossil CO2 emissions into the atmosphere. If 70% of the sorted plastics will be recycled, this will lead to GHG savings of 29,000 to 45,000 ton/year.
In conclusion the Eco+Eco plant will provide an example of MSW management covering an extended and complex area such the Venice Province, with improved sorting technology moving towards “closing the circle”.
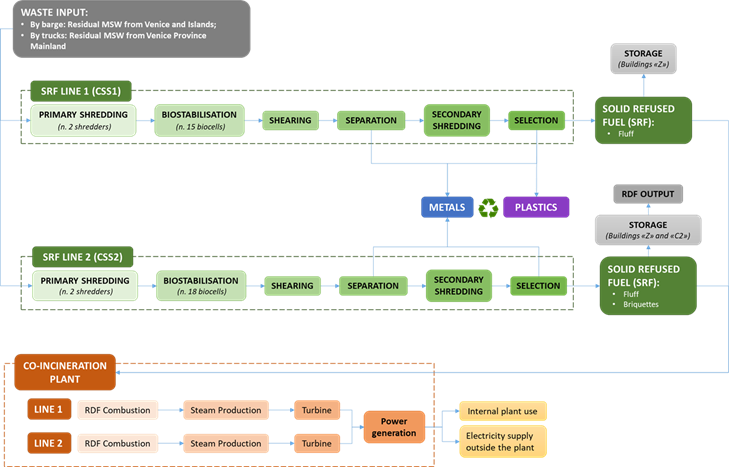
Figure: final flow chart of the plant once revamped


